Private Keys: The Gatekeepers of Blockchain Security
Private keys are one of the most essential elements of blockchain technology. They act as the digital keys that unlock the ability to access and control your assets, verify transactions, and prove ownership within the blockchain world. Whether you’re dealing with Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies, private keys are at the heart of your security.
What is a Private Key?
A private key is a long string of numbers and letters (like a complex password) that gives you control over your cryptocurrency or blockchain account. It acts as proof that you are the owner of a specific wallet or address on the blockchain.
Think of it this way:
- Imagine you have a vault on the blockchain with digital money inside.
- The private key is the only key that can unlock this vault and give you access to your assets.
- If you lose the key, you lose access to the vault forever—and no one can help you retrieve it.
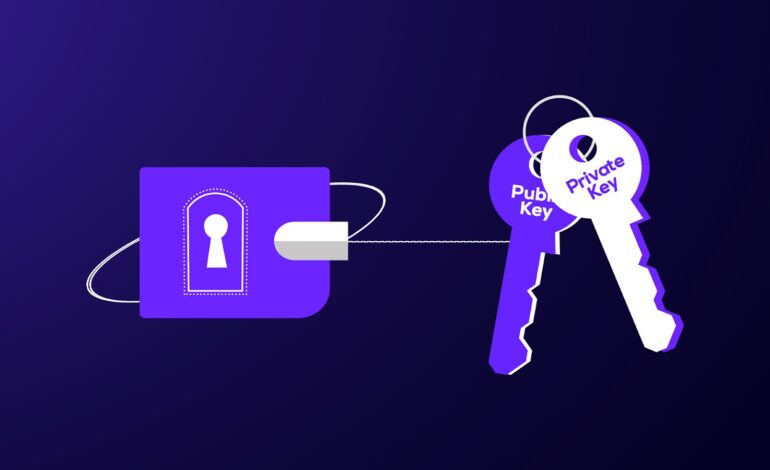
How Private Keys Work with Public Keys
In blockchain, private keys are paired with public keys to create a secure way of sending and receiving transactions.
Here’s a simple analogy:
- Public Key = Your email address: It’s what you share with people so they can send you emails (or, in the case of blockchain, digital assets).
- Private Key = Your email password: It’s what you use to access your inbox and control your emails. You never share this password with anyone.
When you generate a wallet, the system creates:
- A private key (which must be kept secret).
- A public key (which can be shared freely).
The public key allows people to send you assets, and the private key lets you access and control those assets.
Why Private Keys are Critical in Blockchain
Here are a few key reasons private keys are so important:
- Ownership and Control: If you own the private key, you control the corresponding funds or data on the blockchain. Without the private key, you have no access.
- Digital Signatures: Private keys allow you to create a digital signature on transactions, which proves that the transaction was authorized by you and not someone else. These signatures cannot be forged or altered.
- Security through Cryptography: Blockchain systems use public-private key cryptography to ensure the security and authenticity of transactions. Only the person with the correct private key can move funds or execute a smart contract from that wallet.
How Private Keys are Used in Real Life
- Sending Cryptocurrency: When you send Bitcoin or another cryptocurrency, your private key signs the transaction, authorizing it on the blockchain.
- Accessing a Crypto Wallet: Your private key gives you access to your wallet’s balance. Software wallets store the private key for you, while hardware wallets keep it offline for better security.
- Smart Contracts and DeFi Applications: In decentralized finance (DeFi), private keys are used to approve smart contracts that interact with your funds.
The Risks of Losing or Compromising a Private Key
What happens if you lose your private key?
- Lost Forever: If you lose your private key, you lose access to your wallet and all the assets inside—there is no way to recover them. Many people have lost large amounts of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies this way.
What if someone steals your private key?
- Complete Control: If someone gains access to your private key, they can steal your assets or execute unauthorized transactions. This is why keeping your private key safe is critical.
How to Protect Your Private Key
- Use a Hardware Wallet:
- A hardware wallet stores your private key offline, making it immune to online hacks.
- Example: Ledger Nano or Trezor wallets.
- Write Down Your Private Key:
- Write it on paper and store it in a secure place. This is often referred to as a paper wallet.
- Avoid storing private keys on digital devices like smartphones or computers, as they can be hacked.
- Use a Seed Phrase:
- Some wallets generate a 12 or 24-word seed phrase to back up your private key.
- If you lose access to the wallet, the seed phrase allows you to recover your assets.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- If you use an online wallet, enable 2FA to add an extra layer of security.
Real-World Stories of Lost Private Keys
- The $220 Million Lost Bitcoin: A man in Germany lost access to over 7,000 Bitcoin (worth about $220 million) because he forgot the password to his hardware wallet. He had only a few attempts left before the wallet would lock forever.
- The Landfill Hard Drive: A British man accidentally threw away a hard drive containing his private key to over 8,000 Bitcoin. Despite searching through tons of trash in a landfill, he never recovered the drive.
Private keys are your ticket to control and ownership in the blockchain world. They give you access to your digital assets and allow you to prove ownership and authorize transactions. However, with great power comes great responsibility: If you lose your private key, your assets are gone forever. That’s why protecting your private keys is the most critical step for anyone entering the blockchain space.
If you’re new to cryptocurrencies and blockchain, take the time to understand how private keys work and how to protect them. They are the backbone of blockchain security and the difference between owning your digital wealth and losing it forever.