Blockchain is a revolutionary technology, but it faces some serious challenges, especially when it comes to scalability and transaction speed. For blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are now widely adopted, the high demand means these networks often struggle with slow speeds and expensive transaction fees. This is where Layer 2 solutions come into play, offering faster and cheaper alternatives while maintaining the security and decentralization of the underlying blockchain.
What are Layer 2 Solutions?
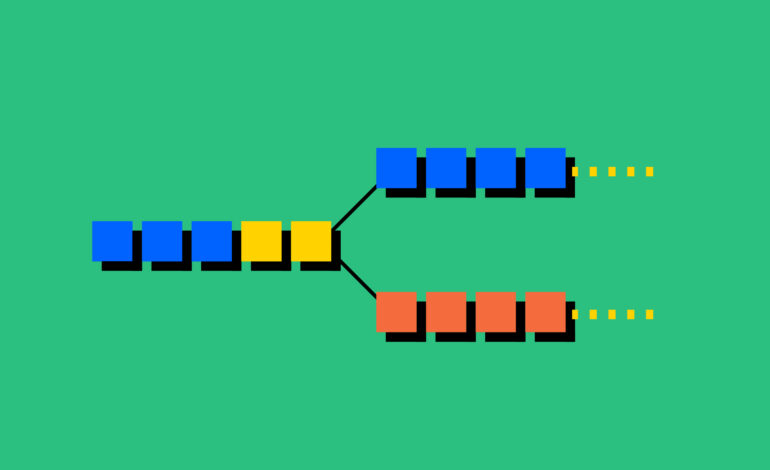
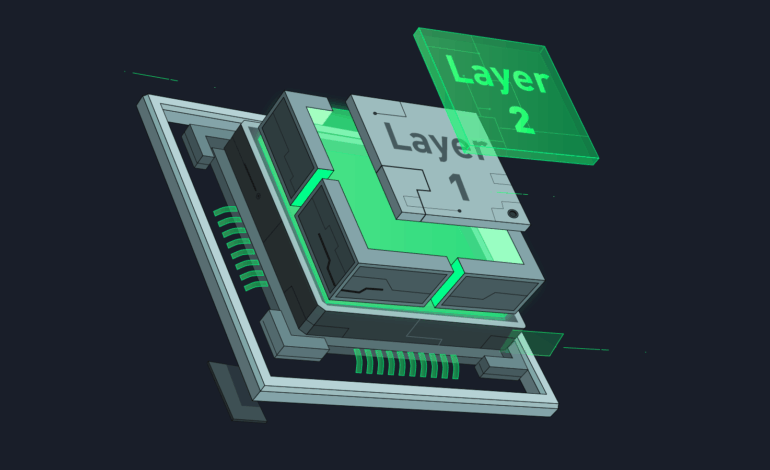
A Layer 2 solution is a secondary framework or protocol that is built on top of an existing Layer 1 blockchain (like Ethereum or Bitcoin). The main goal of Layer 2 is to offload transactions from the main blockchain to reduce congestion, increase speed, and lower fees.
Think of Layer 2 as a side road that handles extra traffic, while the main highway (Layer 1 blockchain) stays less congested and continues functioning efficiently. The Layer 2 protocols still rely on the main blockchain for security and final settlement, but they process most transactions off-chain.
How Does Layer 2 Work?
Instead of recording every transaction on the main blockchain (Layer 1), Layer 2 handles transactions off-chain and only sends a summary or final result to the main blockchain. This reduces the workload on Layer 1, allowing for more transactions to be processed efficiently.
For example:
- On Ethereum, a single transaction might cost several dollars (or even more) during peak times.
- With a Layer 2 solution like Optimism or Arbitrum, the same transaction can cost just a few cents while still being secure.
Benefits of Layer 2 Solutions
- Lower Fees: With fewer transactions crowding the main chain, fees are reduced for users.
- Faster Transactions: Transactions processed off-chain are faster because they bypass the congestion of Layer 1.
- Increased Scalability: Layer 2 increases the overall capacity of the network to handle more users and applications.
- Security: Layer 2 solutions still leverage the security of the underlying blockchain, ensuring trust and decentralization.
Types of Layer 2 Solutions
There are several types of Layer 2 solutions, each offering unique ways to enhance blockchain performance:
1. State Channels
- How It Works: A state channel allows users to conduct multiple transactions off-chain and only post the final result on the blockchain.
- Example: Imagine two people betting on multiple games. Instead of recording each bet on the blockchain, only the final balance after all games is recorded.
- Real-World Example: Lightning Network on Bitcoin and Raiden Network on Ethereum.
2. Sidechains
- How It Works: A sidechain is an independent blockchain connected to the main blockchain (Layer 1) via a bridge. Users can move assets between the two blockchains.
- Example: Sidechains handle specific transactions (like gaming or NFT transfers) to reduce congestion on Layer 1.
- Real-World Example: Polygon (formerly Matic), which helps Ethereum handle more transactions.
3. Rollups (Optimistic and ZK-Rollups)
- How They Work: Rollups bundle multiple transactions together and submit them as one to the main blockchain.
- Optimistic Rollups: Assume transactions are valid by default but allow for fraud challenges if necessary.
- ZK-Rollups: Use zero-knowledge proofs to ensure all transactions are valid without needing challenges.
- Real-World Example: Arbitrum and Optimism (Optimistic Rollups), zkSync (ZK-Rollups).
4. Plasma
- How It Works: Plasma creates child chains connected to the main blockchain. These child chains handle large volumes of transactions and periodically submit the final state to Layer 1.
- Real-World Example: OMG Network uses Plasma to scale Ethereum transactions.
Challenges of Layer 2 Solutions
- Complexity: Layer 2 solutions add extra layers of complexity for developers and users.
- Security Risks: Some Layer 2 protocols are still experimental and may have vulnerabilities.
- Bridging Assets: Moving assets between Layer 1 and Layer 2 (or between Layer 2 networks) can sometimes be slow or costly.
Popular Layer 2 Networks Today
- Polygon: A popular Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, used in gaming and NFT platforms.
- Optimism and Arbitrum: Optimistic rollup solutions focused on reducing Ethereum’s congestion.
- zkSync: A ZK-rollup solution offering high scalability and low fees
When to Use Layer 2 Solutions?
Layer 2 solutions are ideal for:
- Frequent and small transactions: Example: Payments or micro-transactions where high Layer 1 fees are impractical.
- DeFi applications: Decentralized exchanges and lending platforms can operate more smoothly on Layer 2.
- NFT marketplaces: For minting, trading, or transferring NFTs without paying high gas fees.
Future of Layer 2
The future of blockchain scalability lies in Layer 2 adoption. As more users and applications move to Layer 2 solutions, networks like Ethereum 2.0 will likely become more efficient, with Layer 1 serving as the foundation for security and settlement. Layer 2 will be the go-to infrastructure for applications that require speed, low fees, and scalability.
Layer 2 solutions are essential for the growth of blockchain technology, offering the speed and cost-effectiveness necessary for mainstream adoption. As the blockchain ecosystem evolves, understanding how Layer 2 solutions work will become increasingly important for developers, businesses, and users alike.
By offloading transactions from the main blockchain, Layer 2 ensures that blockchain technology can scale without compromising security or decentralization. Whether it’s payment systems, DeFi platforms, or NFT marketplaces, Layer 2 solutions are paving the way for a faster and more efficient future in the blockchain space.